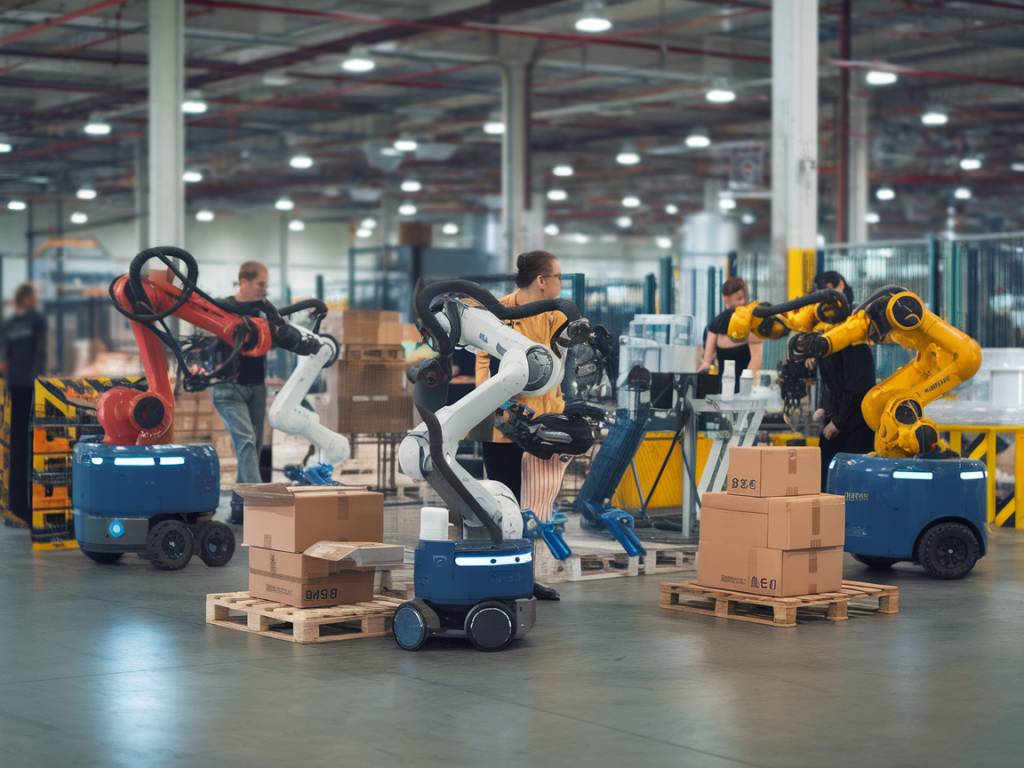
The integration of robotics in warehousing has revolutionized the logistics and supply chain industry. These advancements have primarily focused on boosting efficiency and reducing operational costs, enabling companies to maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving marketplace. This article delves into the various ways robotics is transforming warehousing, highlighting key benefits, challenges, and future implications.
The Rise of Robotics in Warehousing
Over the past decade, the adoption of robotics in warehousing has surged. This rise can be attributed to several factors, including the exponential growth of e-commerce, increasing labor costs, and the necessity for rapid and accurate order fulfillment. As consumer expectations for quicker delivery times and higher accuracy climb, businesses are compelled to adopt innovative solutions to meet these demands.
Advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) have provided the foundational elements that power modern robotic systems. These technologies enable robots to perform a variety of tasks, such as picking, packing, sorting, and transporting goods, with unprecedented speed and precision.
Key Benefits of Robotics in Warehousing
Robotic systems offer numerous advantages that contribute to the improvement of warehousing operations. Some of the most significant benefits include:
- Increased Efficiency: Robots can work around the clock without fatigue, significantly increasing the speed of operations. This 24/7 operation capacity allows for faster order processing and reduces turnaround times.
- Accuracy and Precision: Advanced sensors and AI algorithms enable robots to handle goods with a high degree of accuracy, minimizing the risk of errors in picking and packing processes.
- Cost Reduction: The initial investment in robotic technology can be substantial, but the long-term savings on labor costs and efficiency gains often outweigh these initial expenses. Automation also reduces the need for temporary staffing during peak periods, providing more predictable and stable labor costs.
- Enhanced Safety: Robots take over physically demanding and repetitive tasks, reducing the risk of workplace injuries. This improves overall workplace safety and leads to a healthier workforce.
- Optimized Space Utilization: Robotic systems can operate in tighter spaces and utilize vertical storage more effectively than human workers. This maximizes the use of available warehouse space.
Types of Warehouse Robots
Various types of robots are used in warehousing, each designed to perform specific tasks. Here are some common categories:
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): These are used to transport goods within the warehouse. They follow predefined paths using sensors or wires embedded in the floor, ensuring consistent and efficient movement of materials.
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): These systems include robotic cranes and shuttles that store and retrieve goods from high-density storage racks. They enhance storage efficiency and reduce the time required to access items.
- Sorting Robots: These robots use advanced algorithms to recognize and sort items based on various criteria such as size, weight, and destination. They are commonly used in fulfillment centers to streamline the sorting process.
- Picking Robots: Equipped with advanced vision systems and grippers, these robots can identify and pick items from shelves with high accuracy. They are particularly useful in order fulfillment and inventory management.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Designed to work alongside human workers, cobots assist with various tasks, enhancing human capabilities and improving overall efficiency.
Challenges in Implementing Robotics in Warehousing
While the benefits of robotics in warehousing are substantial, there are several challenges that companies must navigate when implementing these technologies:
- High Initial Investment: The cost of purchasing and installing robotic systems can be significant, posing a barrier for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). However, the return on investment (ROI) typically justifies the initial expenditure over time.
- Integrating with Existing Systems: Legacy systems and infrastructure may not be compatible with advanced robotic technologies, necessitating significant upgrades and modifications. This integration process can be time-consuming and costly.
- Skilled Workforce: The operation and maintenance of robotic systems require specialized skills. Companies must invest in training their workforce or hiring skilled personnel, which can add to the overall cost.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance of robotic systems. This involves additional costs and resources, which must be accounted for in the overall budget.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As robotic systems become more connected through IoT and other networked environments, they become potential targets for cyberattacks. Robust cybersecurity measures must be implemented to protect these systems.
The Future of Robotics in Warehousing
The future of robotics in warehousing is promising, with ongoing advancements poised to further enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Key trends and innovations to watch include:
- AI and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and ML will enable robots to become more autonomous and capable of making real-time decisions. This will further streamline operations and minimize human intervention.
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will facilitate faster and more reliable communication between robotic systems and central control units. This will enhance the coordination and responsiveness of warehouse operations.
- Edge Computing: Leveraging edge computing will allow data processing to occur closer to the source, reducing latency and improving the efficiency of robotic systems.
- Enhanced Human-Robot Collaboration: Future developments will focus on improving the synergy between human workers and robots. This collaboration will combine human ingenuity with robotic precision for even greater efficiency.
- Scalability: Robotic systems will become more modular and scalable, allowing businesses to easily expand or adjust their operations based on demand without significant infrastructure changes.
In conclusion, the adoption of robotics in warehousing has already proven to be a game-changer in the logistics and supply chain industry. The benefits of increased efficiency, cost reduction, enhanced safety, and optimized space utilization are profound. While challenges remain, continuous innovations and advancements hold the promise of overcoming these hurdles, paving the way for a more efficient and cost-effective future in warehousing operations.
Summary: The integration of robotics in warehousing enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and improves accuracy. Key benefits include 24/7 operation, increased safety, and space optimization. Challenges involve high initial investment and the need for skilled maintenance. Ongoing advancements in AI, 5G, and human-robot collaboration herald a promising future for warehouse robotics.