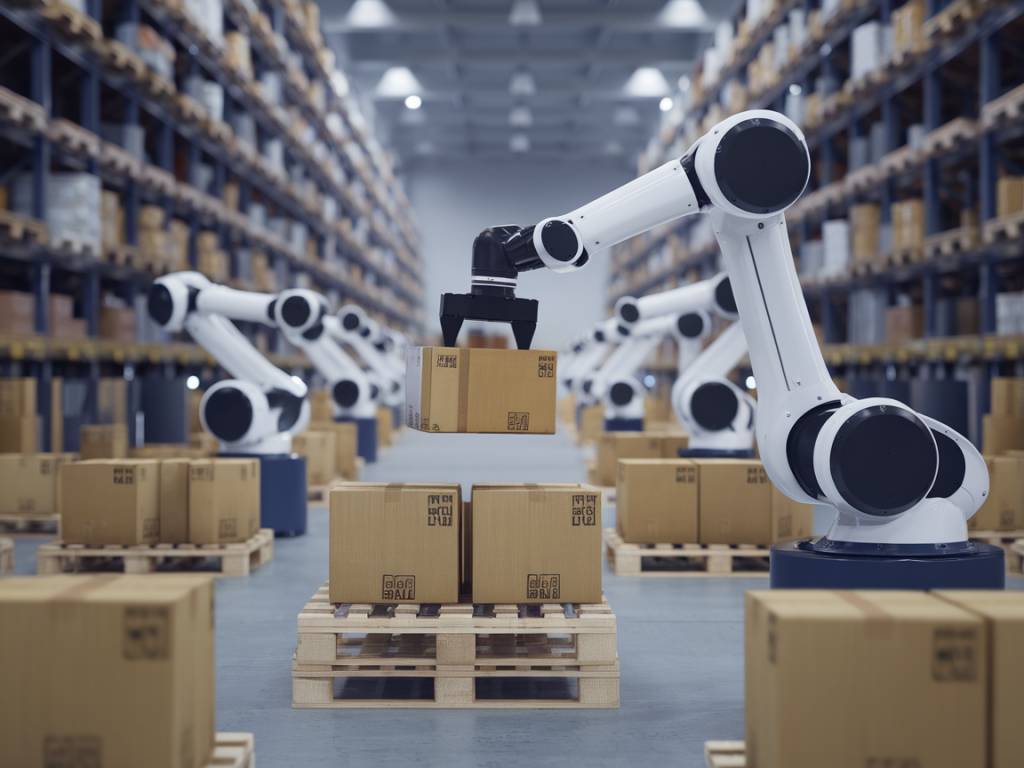
The logistics sector is undergoing a transformative shift as it adapts to persistent labor shortages. These shortages, driven by an aging workforce, rising e-commerce demands, and a decreasing interest in manual labor jobs, are pushing companies to seek innovative solutions. Automation is emerging as a critical strategy to address these challenges, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring the continuity of operations.
The Growing Labor Shortage in Logistics
The shortage of labor in logistics is not a recent phenomenon but has been exacerbated by several concurrent factors. The aging population in many developed countries has led to a significant number of retirements, outpacing the entry of younger workers into the sector. Simultaneously, the boom in e-commerce has drastically increased the demand for quick and reliable logistics services, putting additional strain on an already stretched workforce.
Traditional recruitment efforts have struggled to fill roles in warehousing, transportation, and overall supply chain management. Many potential workers are deterred by the physical demands and perceived instability of logistics jobs. The COVID-19 pandemic further complicated the situation, as health concerns and lockdowns shifted consumer behavior heavily towards online shopping, creating a pressing need for more efficient logistics operations.
Automation as a Solution
Automation technology presents a promising avenue to mitigate these issues by filling gaps left by labor shortages. Automation encompasses a broad range of technologies, including robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and advanced data analytics, all of which have unique applications in logistics.
- Robotics: Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), and robotic arms can perform tasks such as picking, packing, and transporting goods within warehouses. These robots enhance efficiency and accuracy while reducing the physical burden on human workers.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms can optimize routing, predict demand, and improve inventory management. Machine learning models analyze large datasets to forecast trends, allowing logistics companies to proactively address potential issues.
- Data Analytics: Advanced analytics provide insights into every aspect of the supply chain, from procurement to delivery. Real-time data monitoring ensures that businesses can make informed decisions quickly, further reducing dependency on a large workforce.
Case Studies of Automation in Logistics
Several companies have successfully integrated automation into their logistics operations, serving as benchmarks for the industry.
Amazon
Amazon’s fulfillment centers are a prime example of effective automation. The e-commerce giant uses over 200,000 robots alongside human workers to handle a vast array of tasks. These robots can carry packages, sort products, and even manage inventory, significantly speeding up the fulfillment process.
UPS
UPS has invested heavily in automation and AI to enhance its delivery systems. The company uses predictive analytics for route optimization and sorting automation to handle the 20 million packages it delivers daily. These technologies have allowed UPS to reduce delivery times and enhance overall efficiency.
Benefits of Automation in Logistics
The benefits of automation extend beyond merely addressing labor shortages. They contribute to overall improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings.
- Increased Efficiency: Robots and automation systems can operate continuously without fatigue, significantly increasing the speed of operations. This is particularly beneficial during peak periods, such as holiday seasons, where demand spikes dramatically.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Automated systems reduce human error, particularly in repetitive tasks such as inventory management and order picking. This leads to fewer mistakes, ensuring that customers receive the correct products on time.
- Cost Savings: Although the initial investment in automation technology can be substantial, the long-term savings are significant. Companies can reduce labor costs, minimize product losses from errors, and enhance overall productivity, leading to a better return on investment.
Challenges and Considerations
While automation offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges that companies must address to ensure successful implementation.
Initial Investment: The cost of purchasing and integrating automation technologies can be high. Businesses must carefully consider their financial capacity and potential ROI before committing to extensive automation.
Training and Adaptation: Existing employees need to be retrained to work alongside their new robotic counterparts. This requires a shift in skills from manual labor to roles focused on supervision, maintenance, and oversight of automated systems.
Technological Integration: Integrating new technologies with existing systems can be complex. Companies must ensure that their IT infrastructure can support the additional data processing and connectivity requirements of automated systems.
The Future of Automation in Logistics
The future of logistics is increasingly interconnected with automation and digital transformation. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated and capable systems to emerge. Some future trends include:
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices can provide real-time data on the condition and location of goods, enabling more precise tracking and management throughout the logistics chain. This connectivity allows for better coordination between different automated systems and human workers.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers secure, transparent, and immutable record-keeping, crucial for traceability and trust in supply chains. By integrating blockchain with automation, companies can enhance the reliability and security of their logistics operations.
Advanced Robotics
Future robots will have increased capabilities, including enhanced mobility, dexterity, and intelligence. This will enable them to perform a wider range of tasks and adapt to changing conditions, further reducing the need for human intervention.
In conclusion, automation is proving to be an essential tool in overcoming labor shortages in logistics. By improving efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness, automated systems are helping to fill the gap left by a dwindling workforce. As technology continues to advance, the role of automation in logistics will only become more integral, shaping the future of the industry.
Summary: The article explores how automation is addressing labor shortages in logistics. It highlights the benefits of robotics, AI, and data analytics, along with case studies of companies like Amazon and UPS. Challenges, potential future trends, and the overall positive impact of automation on efficiency and cost savings are discussed.