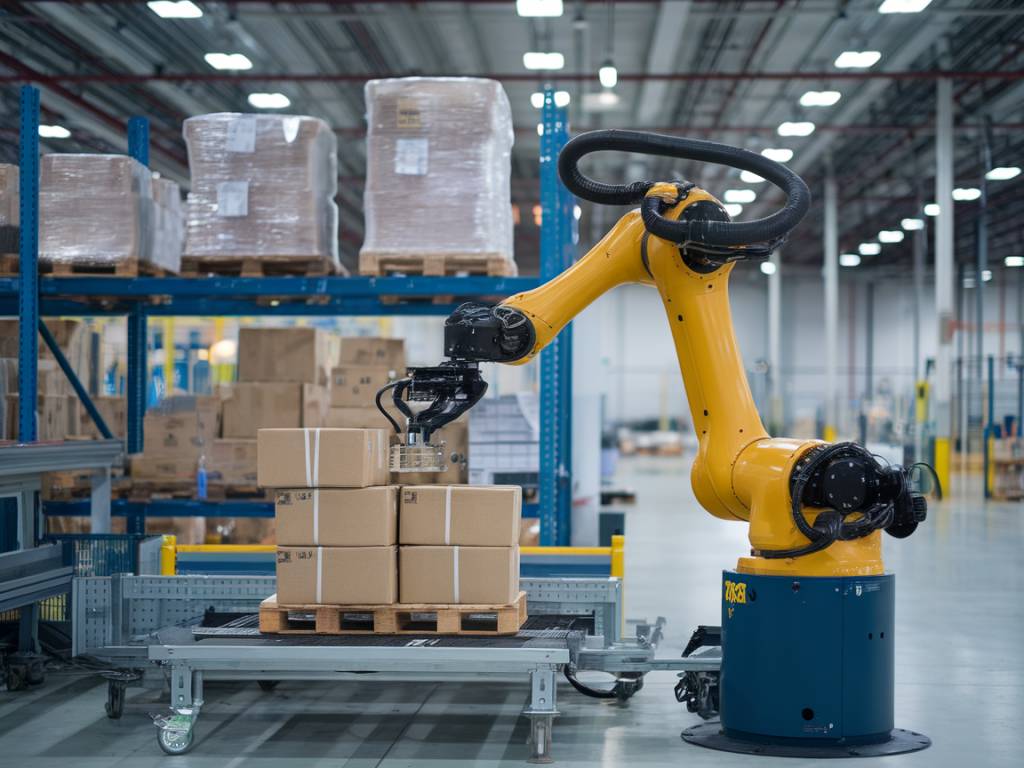
In the fast-paced world of logistics, minimizing human error is crucial for maintaining efficiency and ensuring timely deliveries. Human mistakes, whether due to oversight, fatigue, or misunderstanding, can lead to significant disruptions, increased costs, and unsatisfied customers. The implementation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is quickly becoming a key strategy in mitigating these errors and optimizing logistics operations.
The Concept of Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to the use of software bots to automate routine, rule-based tasks that were traditionally performed by humans. Unlike traditional automation, which often requires extensive programming and integration, RPA leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to handle tasks dynamically. These tasks can range from data entry to order processing and even customer interactions.
In the logistics sector, RPA can be utilized for various functions such as inventory management, order tracking, customer service, and shipment scheduling. By automating these processes, companies can significantly reduce the likelihood of human error while freeing up staff to focus on more complex, value-added activities.
Advantages of RPA in Logistics
The implementation of RPA in logistics offers several distinct advantages, making it an attractive solution for companies seeking to enhance their operational efficiency. Some key benefits include:
- Improved Accuracy: RPA bots are programmed to follow strict guidelines, ensuring data is processed accurately and consistently every time. This reduces the occurrence of errors that can arise from manual data entry or miscommunication.
- Increased Efficiency: With RPA handling repetitive tasks, processes that previously took hours can be completed in a matter of minutes. This increase in speed allows for faster fulfillment times and can improve overall customer satisfaction.
- Cost Savings: By reducing the need for manual labor, RPA can help companies lower operational costs. Additionally, fewer errors translate to fewer resources spent on rectifying mistakes, further contributing to cost efficiency.
- Enhanced Compliance: Logistics operations must adhere to various regulations and standards. RPA ensures that these requirements are consistently met, reducing the risk of compliance breaches and associated penalties.
- Scalability: RPA solutions can be easily scaled up or down based on the needs of the business. This flexibility is particularly useful for companies dealing with fluctuating demand or seasonal peaks.
Applications of RPA in Logistics
RPA can be integrated into numerous aspects of logistics operations, each providing specific benefits and improvements. Here are some key areas where RPA can make a significant impact:
Inventory Management
Inventory management is a critical component of logistics, requiring accurate and timely updates to ensure that stock levels are maintained and replenishment is correctly timed. RPA can automate the monitoring of inventory levels, triggers for reordering, and updates to stock records. This reduces the risk of stockouts or overstock situations, optimizing inventory control.
Order Processing
Processing orders manually can be time-consuming and prone to errors. RPA can automate the entire order-to-fulfillment process, from order capture and validation to updating the warehouse management system and generating shipping labels. By streamlining these processes, companies can reduce order processing times and improve order accuracy.
Customer Service
Customer inquiries, tracking requests, and returns processing can be efficiently managed using RPA. Bots can handle routine customer interactions, provide real-time updates on order status, and manage returns authorization, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex customer issues. This can lead to improved customer satisfaction and faster response times.
Shipment Scheduling and Tracking
Coordinating shipments and tracking deliveries involves multiple steps and can be prone to errors if managed manually. RPA can automate the scheduling of shipments, the generation of tracking numbers, and the updating of delivery statuses. This ensures that shipments are efficiently coordinated and customers receive accurate, timely updates on their deliveries.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing RPA
While RPA offers numerous benefits, its implementation is not without challenges. Companies must carefully plan and execute their RPA initiatives to ensure successful deployment. Some common challenges include:
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many logistics companies use legacy systems that may not readily integrate with RPA solutions. Overcoming this challenge may require custom integration solutions or gradual system upgrades.
- Change Management: Transitioning from manual processes to automated ones can be met with resistance from employees. Effective change management strategies, including training and clear communication, are essential to ensure that the workforce is on board with the new technologies.
- Initial Costs: The upfront costs associated with implementing RPA can be significant. However, these costs are often offset by the long-term savings and efficiency gains. It is important to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis prior to investment.
- Data Security: Automated processes often involve sensitive information. Ensuring that RPA systems are secure and compliant with data protection regulations is critical to maintaining trust and avoiding data breaches.
Future Trends in RPA and Logistics
The future of RPA in logistics is promising, with advancements in technology likely to expand its capabilities and applications. Some potential future trends include:
Intelligent Automation
Combining RPA with artificial intelligence and machine learning can create intelligent automation systems capable of handling more complex tasks and making data-driven decisions. This could further reduce the reliance on human intervention and increase operational efficiency.
Integration with Internet of Things (IoT)
Integrating RPA with IoT devices can provide real-time data and insights into logistics operations. For example, IoT sensors on shipments can provide real-time updates on location and condition, which RPA systems can use to optimize routing and ensure timely deliveries.
Enhanced Predictive Analytics
RPA systems integrated with predictive analytics can help logistics companies anticipate demand, optimize inventory levels, and improve demand forecasting. This can lead to more efficient resource allocation and reduced operational costs.
Human-RPA Collaboration
As RPA continues to evolve, the collaboration between human workers and robots will become more seamless. Humans will focus on higher-level strategic tasks while RPA handles routine activities, leading to a more efficient and productive workforce.
In summary, the integration of Robotic Process Automation in logistics offers numerous benefits, including improved accuracy, increased efficiency, and cost savings. By automating routine tasks, companies can minimize human error and enhance overall operational performance. As technology continues to advance, the potential applications and benefits of RPA in the logistics sector are expected to grow, providing even greater opportunities for optimization and innovation.