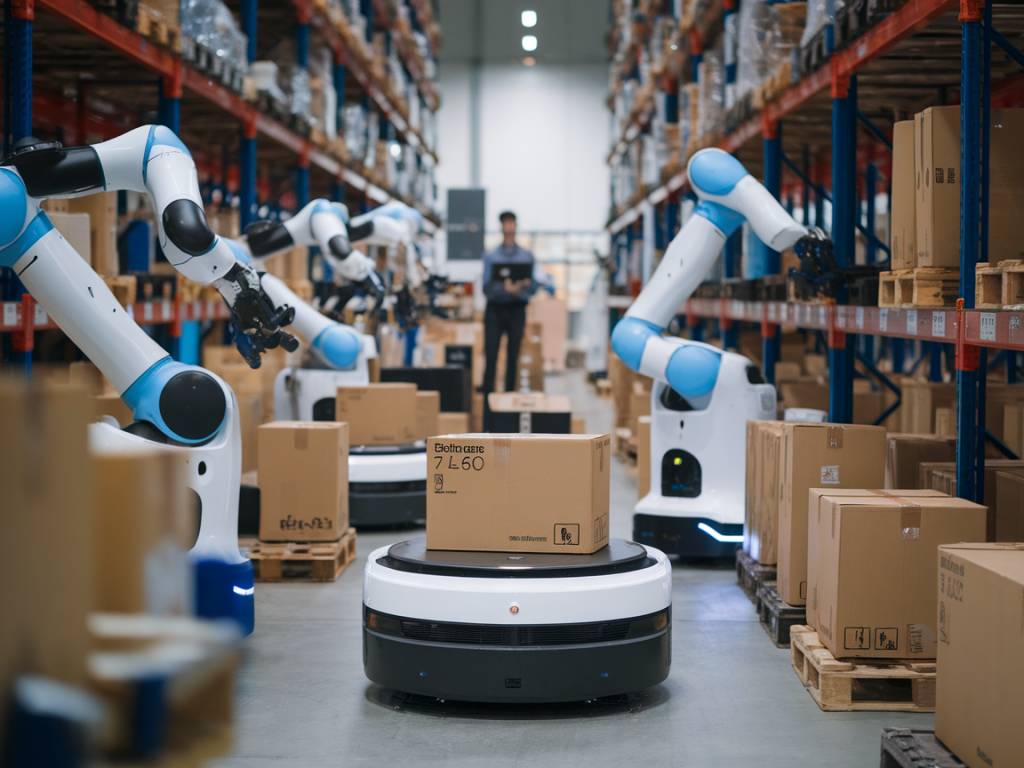
The logistics industry is undergoing a transformative phase, powered by advancements in technology. Among the most significant of these advancements is the convergence of 5G and automation. As these technologies mature, they are poised to revolutionize the way logistics operations are conducted, offering unprecedented efficiency, precision, and adaptability.
Understanding 5G and Its Capabilities
5G, the fifth generation of mobile network technology, offers substantial improvements over its predecessors. With higher data speeds, reduced latency, and greater connectivity, 5G is capable of accommodating the increasing demands of modern logistics operations.
Key features of 5G include:
- High Speed: 5G can provide speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G, allowing for real-time data processing and transmission.
- Low Latency: Latency as low as one millisecond ensures near-instantaneous communication between devices.
- Massive Connectivity: 5G can connect a vast number of devices simultaneously, facilitating the Internet of Things (IoT) in logistics environments.
Automation in Logistics
Automation in logistics utilizes technology to perform tasks that were traditionally managed by human labor. This includes warehouse operations, transportation, and last-mile delivery. Automation comes in various forms, including robotics, autonomous vehicles, and AI-driven software.
Some of the major benefits of automation in logistics are:
- Increased Efficiency: Automated systems can operate 24/7 without breaks, leading to improved productivity and faster processing times.
- Cost Reduction: Reduced reliance on human labor and optimized resource utilization contribute to lower operational costs.
- Improved Accuracy: Automation minimizes human error, leading to higher accuracy in inventory management, order fulfillment, and delivery.
The Synergy Between 5G and Automation
The convergence of 5G and automation is particularly impactful in the logistics industry. 5G’s high speed and low latency make it an ideal enabler for automated systems that require real-time data and constant connectivity. Here are some ways in which this synergy is beneficial:
- Enhanced Communication: 5G enables seamless communication between automated systems, ensuring synchronized operations across the supply chain.
- Real-Time Tracking: With 5G, logistics companies can track shipments in real time, providing more accurate ETAs and improved customer satisfaction.
- Remote Operations: 5G facilitates remote monitoring and management of automated systems, reducing the need for onsite personnel.
- Advanced Analytics: The increased data transmission capabilities of 5G support advanced analytics, helping businesses to make informed decisions rapidly.
Applications in Warehousing
In warehousing, the integration of 5G and automation can lead to the creation of smart warehouses. These facilities utilize automated guided vehicles (AGVs), drones, and robotic arms, all interconnected via a 5G network to optimize operations.
Applications include:
- Automated Sorting: AGVs and robotic arms can sort and move inventory with high efficiency and precision.
- Drones for Inventory Management: Drones equipped with 5G connectivity can perform real-time inventory counts, reducing the need for manual checks.
- Predictive Maintenance: 5G-enabled sensors can monitor equipment health and predict maintenance needs, preventing costly downtimes.
Applications in Transportation
For transportation, 5G and automation enable the development of autonomous vehicles and smart fleets. These advancements are crucial for enhancing the efficiency and safety of logistics operations.
Examples of applications include:
- Autonomous Trucks: Autonomous trucks can navigate highways and urban routes with greater efficiency, reducing transit times and lowering fuel consumption.
- Intelligent Fleet Management: 5G connectivity allows for real-time tracking and optimization of fleet routes, improving delivery times and reducing operational costs.
- Enhanced Safety: Automated vehicles equipped with 5G can communicate with each other and with traffic infrastructure, enhancing safety through coordinated movements.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promising prospects, the integration of 5G and automation in logistics is not without challenges. Some key considerations include:
- Security Concerns: The increased connectivity exposes systems to potential cyber threats, necessitating robust cybersecurity measures.
- Infrastructure Requirements: Implementing 5G networks and automation systems requires significant investment in infrastructure and technology.
- Regulatory Compliance: Logistics companies must navigate complex regulatory landscapes to deploy autonomous systems, especially in transportation.
- Skilled Workforce: The shift towards automated processes demands a workforce proficient in managing and maintaining advanced technologies.
Future Outlook
As 5G technology becomes more widespread and automation techniques continue to evolve, the logistics industry stands on the brink of a new era. Companies that embrace these advancements will likely gain a competitive edge through improved operational efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced customer experiences.
Looking ahead, potential developments include:
- Fully Automated Supply Chains: End-to-end automation, supported by 5G, could streamline the entire logistics process from production to delivery.
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: Advanced AI algorithms can further optimize automated systems, predicting demand and adapting in real time.
- Expansion of IoT: The proliferation of IoT devices, all interconnected via 5G, will offer deeper insights and greater control over logistics operations.
The convergence of 5G and automation heralds a transformative period for the logistics industry, promising enhanced efficiency and innovation. Organizations poised to adopt these technologies will find themselves at the forefront of a rapidly evolving market.
Summary: The convergence of 5G and automation is set to revolutionize the logistics industry by enabling real-time communication, enhanced efficiency, and innovative applications in warehousing and transportation. Companies should prepare to navigate challenges such as security and regulatory compliance to leverage these advancements fully.