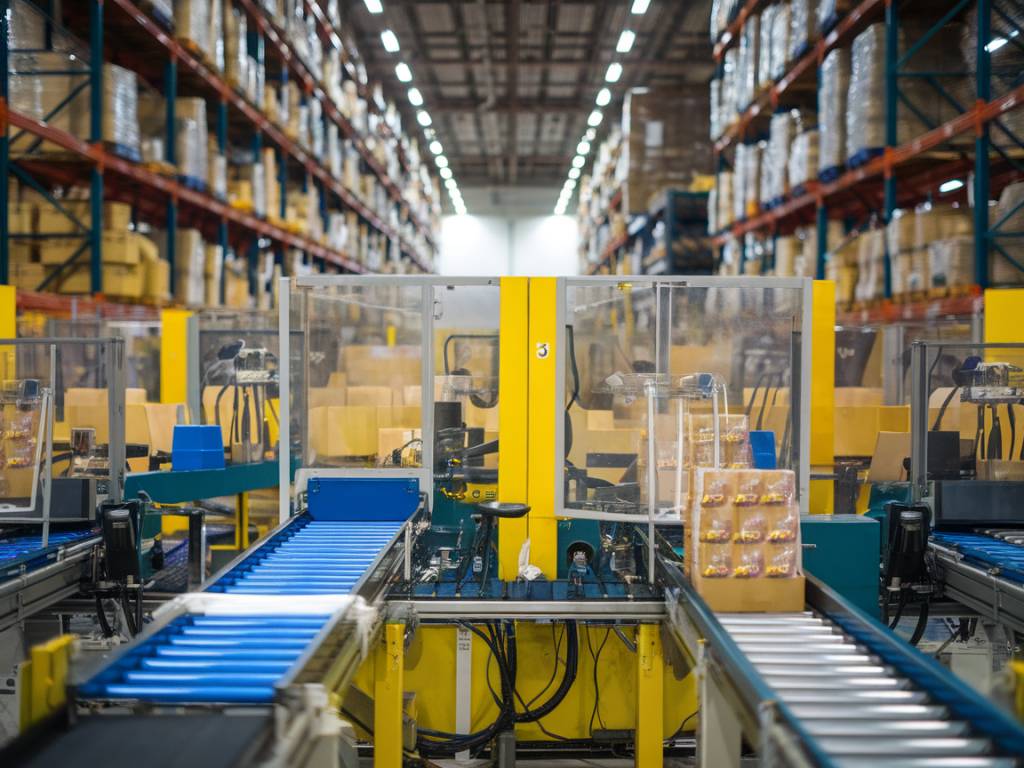
Automated packaging in logistics has undergone significant transformation over the last few decades, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and the global increase in e-commerce. This article delves into the history, current state, and future prospects of automated packaging in logistics, providing a thorough understanding of its impact on the industry.
Historical Background of Automated Packaging
The concept of automated packaging began materializing in the mid-20th century. Initially, packaging was a labor-intensive process, relying heavily on manual labor for tasks such as sealing, labeling, and boxing products. Automated packaging systems emerged out of a necessity to increase efficiency and reduce labor costs. Early systems were rudimentary, involving simple machinery that could perform basic tasks like automated sealing.
The 1980s marked the beginning of significant technological integration in packaging processes. The advent of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) allowed for more precise control and automation of packaging lines. The implementation of these controllers made it possible to program machines to handle a variety of packaging tasks, significantly enhancing productivity and accuracy.
Technological Advancements Shaping Automated Packaging
The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed remarkable technological advancements that profoundly impacted automated packaging. Here are some key technologies that have shaped the industry:
- Robotics: The introduction of robotics in packaging has revolutionized the industry. Robots can perform multiple tasks such as picking, placing, sorting, and palletizing with remarkable speed and precision. They are particularly useful in handling delicate or heavy products, thereby reducing the risk of damage and worker injury.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms enable packaging machines to adapt and optimize operations based on real-time data. These technologies help in predicting equipment maintenance needs, thus minimizing downtime. They also aid in improving packaging design and material usage, thereby reducing waste.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT technology facilitates seamless communication between various devices on the packaging line. Sensors and smart devices collect and transmit data to a central system, allowing for real-time monitoring and control of the packaging process. This connectivity ensures that any issues are promptly identified and addressed, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Vision Systems: Advanced vision systems are critical for quality control in automated packaging. These systems use cameras and sensors to inspect products for defects, correct labeling, and proper sealing. They ensure that only products meeting quality standards reach the consumer.
- 3D Printing: Although still emerging, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize packaging by enabling the rapid production of customized packaging solutions. This technology is particularly valuable for small-batch production and prototyping.
The Role of Automated Packaging in Modern Logistics
Automated packaging plays a crucial role in modern logistics, directly impacting efficiency, cost management, and customer satisfaction. Here are some of the benefits:
- Efficiency and Speed: Automated packaging significantly reduces the time required to package products, thereby speeding up the entire supply chain process. High-speed packaging machines can handle thousands of packages per hour, far surpassing the capabilities of manual labor.
- Cost Reduction: By automating packaging processes, companies can reduce labor costs and minimize the risk of human error. Moreover, automation allows for optimal use of packaging materials, reducing waste and lowering material costs.
- Scalability: Automated packaging systems are highly scalable, allowing companies to adjust production levels based on demand. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in managing seasonal peaks and fluctuations in consumer demand.
- Consistency and Quality: Automated systems ensure consistent packaging quality, essential for maintaining brand reputation and customer satisfaction. The use of advanced vision systems and sensors minimizes the risk of defects and errors.
- Safety: Automation reduces the need for manual handling of products, reducing the risk of workplace injuries. Robots and automated machinery can handle dangerous or repetitive tasks, ensuring a safer working environment for employees.
Challenges in Implementing Automated Packaging
Despite the numerous benefits, companies face several challenges when implementing automated packaging systems:
- High Initial Investment: The cost of acquiring and installing automated packaging machinery can be substantial. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), this initial investment may be a significant barrier.
- Technical Expertise: Operating and maintaining automated packaging systems requires specialized technical knowledge. Companies must invest in training their workforce or hiring experts, which can add to the operational costs.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating new automated systems with existing infrastructure and processes can be complex and time-consuming. Companies must ensure seamless compatibility to avoid disruptions in operations.
- Rapid Technological Changes: The fast pace of technological advancements means that packaging systems can become obsolete quickly. Companies must stay updated with the latest technologies to remain competitive, necessitating continuous investment in upgrades and new systems.
Future Trends in Automated Packaging
The future of automated packaging in logistics looks promising, with several emerging trends expected to shape the industry:
- Increased Adoption of AI and Machine Learning: The use of AI and machine learning will continue to grow, enabling smarter and more efficient packaging solutions. These technologies will facilitate better predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Cobots are designed to work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and safety. They are easier to program and deploy than traditional robots, making them accessible to a broader range of companies, including SMEs.
- Sustainable Packaging Solutions: As environmental concerns grow, there will be a greater focus on sustainable packaging. Automated systems will increasingly incorporate green technologies and materials, such as biodegradable packaging and eco-friendly inks.
- Customization and Personalization: Advances in 3D printing and AI will enable more personalized packaging solutions. Companies will be able to create custom packaging for individual customers, enhancing the consumer experience and brand loyalty.
- Integration with Advanced Supply Chain Technologies: Automated packaging will become more integrated with other advanced supply chain technologies, such as blockchain and autonomous vehicles. This integration will lead to more transparent, efficient, and secure supply chains.
In conclusion, the evolution of automated packaging in logistics has been marked by significant technological advancements and growing emphasis on efficiency, cost reduction, and quality. As the industry continues to evolve, companies that embrace these innovations will be better positioned to meet the demands of an ever-changing marketplace.
Summary: This article explores the evolution of automated packaging in logistics, highlighting its history, technological advancements, role in modern logistics, challenges, and future trends. Automated packaging enhances efficiency, reduces costs, ensures quality, and improves safety, making it a critical component of the contemporary supply chain.